AI Bots and Robots.txt
There’s been a lot of discussion lately around AI crawlers and bots, which are used to train LLMs and/or fetch content on behalf of their users. In the past few weeks I’ve seen blog posts about the amount of traffic from these crawlers, techniques and products to control how and what they can crawl, reports of misbehaving crawlers and more. Ironically, there’s even AI based services to mitigate AI crawler bots! Given how much interest there is, I thought I’d try and explore some HTTP Archive data to see how sites are using robots.txt to state their preferences on AI crawling.
Robots.txt
A robots.txt file is located at the root of an origin, and provides instructions for how bots should interact with a website. This practice began in 1994 and quickly became a de facto standard. Years later, Google introduced the Robots Exclusion Protocol, which was standardized in 2022.
A simple example of a robots.txt directive is below. This directive tells a User-Agent with the string GPTBot that it is not permitted to crawl the site.
User-Agent: GPTBot
Disallow: /
It’s important to note that robots.txt does not restrict access to bots by itself, as adherence to it is voluntary. But analyzing the content of these files can provide some insight on the overall sentiment towards AI bots.
How Many Sites use Robots.txt Files?
The HTTP Archive collects page details from millions of websites each month, and uses a custom metric to fetch a robots.txt file from each site. The data from July 2025 shows that 94% of 12 million websites have a robots.txt file containing at least 1 directive. The HTTP Archive’s Web Almanac has an entire chapter on SEO, containing more details around the contents of robots.txt - and is definitely worth a read.
| Sites | % of Sites | |
| Serves a Robots.txt file | 12,155,217 | 94.12% |
| No Robots.txt | 759,409 | 5.88% |
Some bots choose to identify themselves in the User-Agent string of an HTTP request. Others attempt to hide what they are doing, which is one of the reasons why many sites utilize services to block unwanted traffic. This research will focus on robots.txt files, which tell us whether site owners would like to restrict AI bots based on their advertised User-Agent strings.
Many AI services publish the User-Agent strings for this purpose, and also provide guidance on how they adhere to robots.txt directives. Additionally it’s commone for a service to advertise multiple User-Agents since they can be used for different purposes (crawling, responding to user input, etc).
For example
- ChatGPT advertises themselves as
ChatGPT-User,GPTBot, andOAI-SearchBot - Anthropic advertises themselves as
ClaudeBot,Claude-User, andClaude-SearchBot - Apple advertises themselves as
Applebot-Extended
There are many more AI agents, with more showing up all the time - and unfortunately not all of them respect the robots.txt directives. For this research, I’ve used a list of AI Bots from the AI Robots.txt Github repository to determine which robots.txt entries are targeted towards the various AI services.
User-Agents Referenced in Robots.txt
The most popular User-Agent referenced in robots.txt files is simply a wildcard *. In fact 97.4% of robots.txt files have at least 1 directive using this wildcard, often to allow and/or disallow bots to part or all of their site’s content to all bots. Typically the next most frequent group of User-Agents are for search bots (googlebot, bingbot, etc) and SEO bots (mj12bot, ahrefsbot, semrushbot, etc).
Over the past few years, User-Agents for AI Bots have been added to many sites’ robots.txt files. As of July 2025, AI Bots top the list of User Agents referenced across popular sites. In fact almost 21% of the top 1000 websites have rules for ChatGPT’s “GPTBot” in their robots.txt file. There’s an interesting pattern shift around site popularity, with a greater percentage of popular sites having AI bot directives vs a large percentage of SEO bot directives on less popular sites.
The table below breaks this out by site popularity (using Google’s CrUX rank). In the darker shaded areas of this table, you can see many references to bots operated by popular AI services - ChatGPT, Claude, Google, Perplexity, Anthropic, etc.
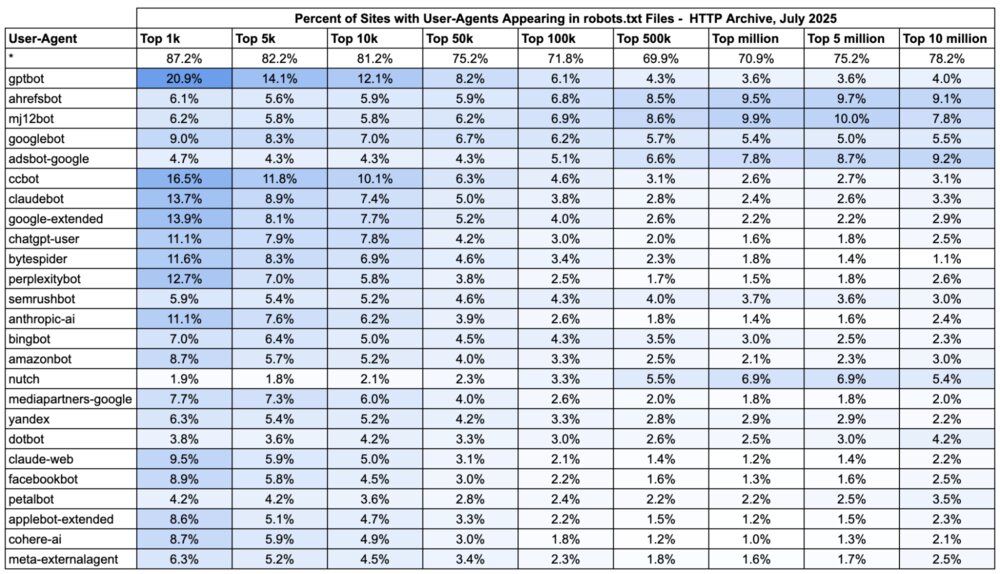
When Did Sites Start Adding AI Crawlers to robots.txt
In August 2023, ChatGPT added documentation about its crawler, including instructions on how site owners can block them. Shortly afterwards, articles with instructions on how to block ChatGPT started appearing, it was discussed in Hacker News and there were also claims that some sites were scrambling to block AI agents. While the claims may have sounded sensational, the numbers supported it. In August 2023 the number of sites that included rules for GPTBot in robots.txt files went from 0 to almost 125k sites! A month later it was 299k sites. By November GPTBot was referenced on 578k websites! That’s a massive increase in a short period of time.
In the tables below you can see the number of websites referencing specific User-Agents in their robots.txt files month to month. Claudebot first appeared in December 2023 on just 2,382 sites (increasing to 30k within 4 months) and PerplexityBot appeared in January 2024 with just 157 sites (increasing to 31k in April 2024). These were not picked up as quickly as GPTBot, which may have been due to limited public awareness of the rise of these models.
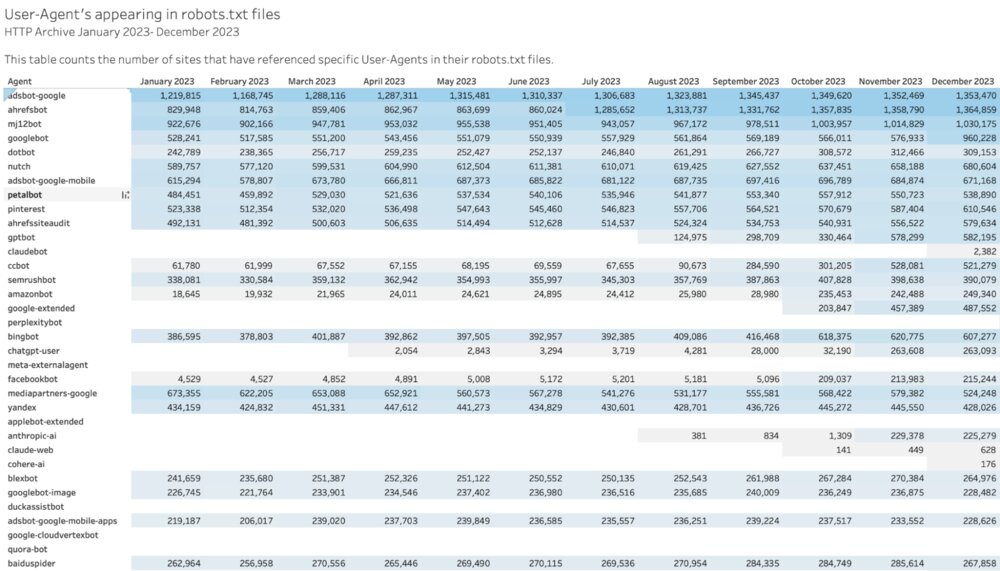
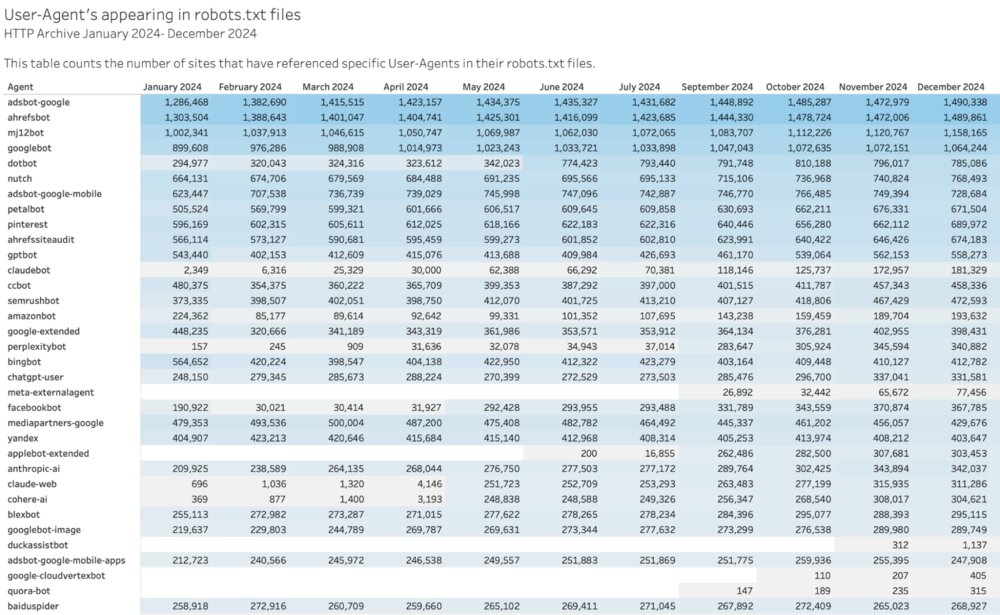
Throughout 2024 you can see that more and more sites include directives for the AI bots. Apple’s crawler was revealed in May 2024, and news reports about it started showing up in June. By September there was almost 262k sites including it in their robots.txt files. Perplexity and Claude also started appearing in over 100k site’s robot.txt in May 2024. And a handful of new ones started appearing as they gained popularity.
That brings us to 2025 where you can see that ChatGPT, Claude, Facebook and others appear in the robots.txt files of over 560k sites! A few newer bots started showing up as well - belonging to Meta, DuckDuckGo, and Quora. This might be due to some services and platforms updating robots.txt files automatically, but it could also be due to more awareness as there have been frequent articles about AI crawlers and bots throughout 2025.
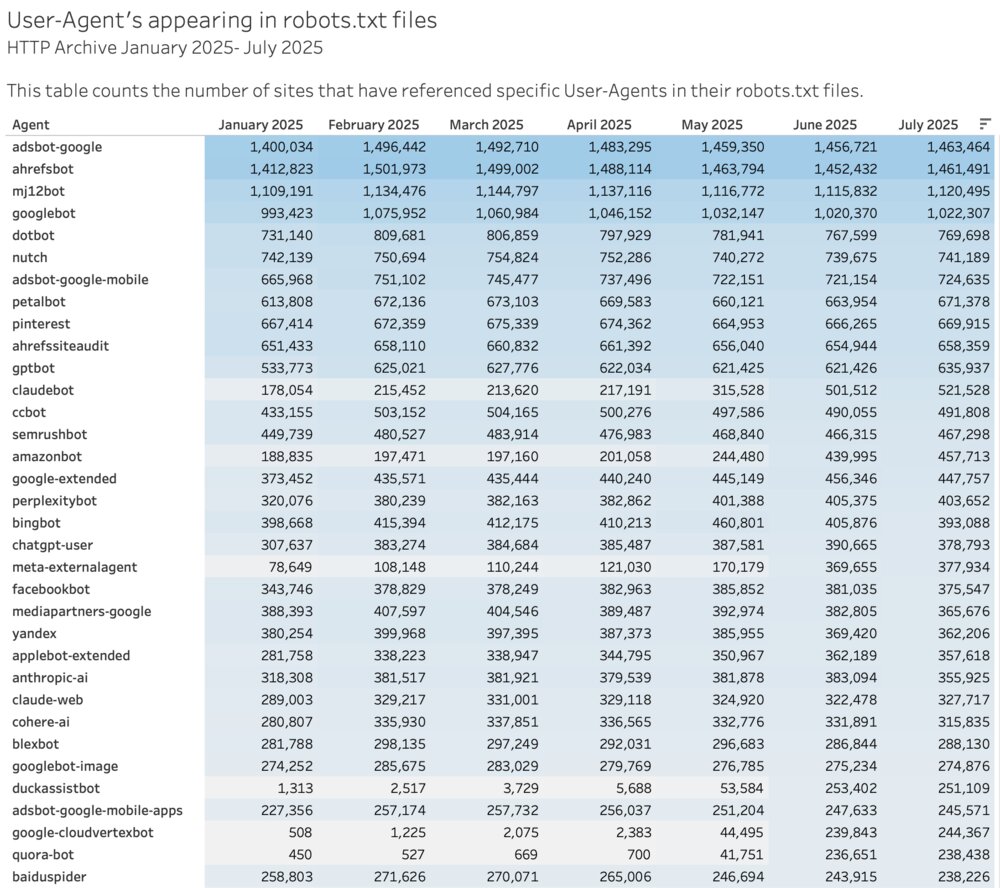
You can explore this data more in this interactive visualization. There are many more User-Agents than what I listed here, and if you scroll down you might spot some newer ones.
To Allow or Not to Allow…
So far we’ve looked at how many websites are including directives for various User-Agents, and we’ve observed substantial growth in the references to AI crawlers and bots. But we’ve also observed a difference in how sites are using them based on popularity. Now let’s look at the types of rules being applied to them.
It’s not uncommon for rules to exist both allowing a bot and disallowing certain paths. So the presence of both could indicate that site owners want to allow those bots to access portions of their sites. For example on Vimeo’s robots.txt file, you can find
# Block Open AI - Allowing specific marketing/informational paths
User-agent: GPTBot
Disallow: /
Allow: /features/
Allow: /solutions/
Allow: /enterprise/
Allow: /integrations/
Allow: /blog/
Allow: /create/
Some sites look to restrict AI traffic, such as this excerpt from Healthline’s robots.txt file -
User-agent: GPTBot
Disallow: /
User-agent: Applebot-Extended
Disallow: /
User-agent: anthropic-ai
Disallow: /
User-agent: Bytespider
Disallow: /
User-agent: CCBot
Disallow: /
User-agent: ClaudeBot
Disallow: /
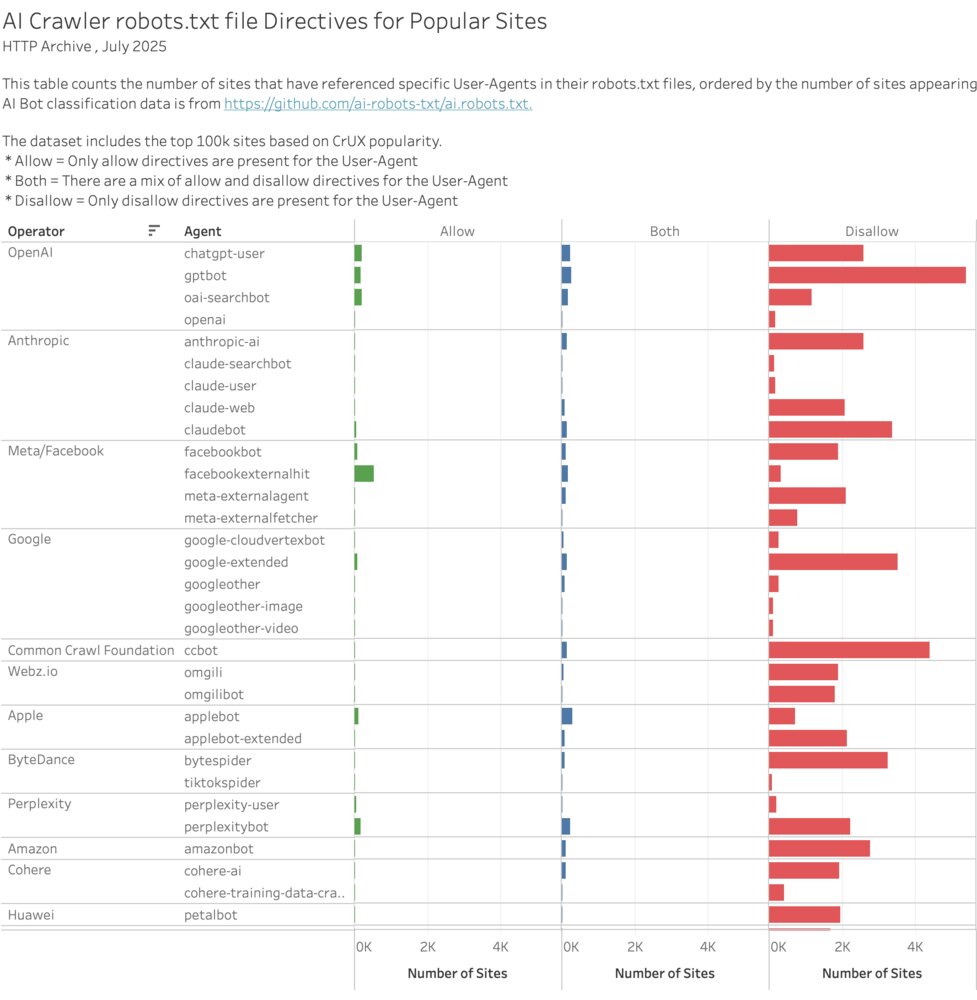
This graph below shows AI Crawler directives for popular websites. From this data we can see that it’s very common for popular websites to attempt to restrict access to AI bots. However, they are not uniform in the bots that they choose to disallow - most of the time only including directives for the most popular AI services.
If we look at this across all sites a new pattern emerges. We can see a lot more sites that have both allow and disallow directives for AI agents. This may be due to large platforms automatically updating these agents in their customer’s robots.txt file. For example, Squarespace and Cloudflare both have solutions that appear to automatically add AI crawlers to a site’s robots.txt file.
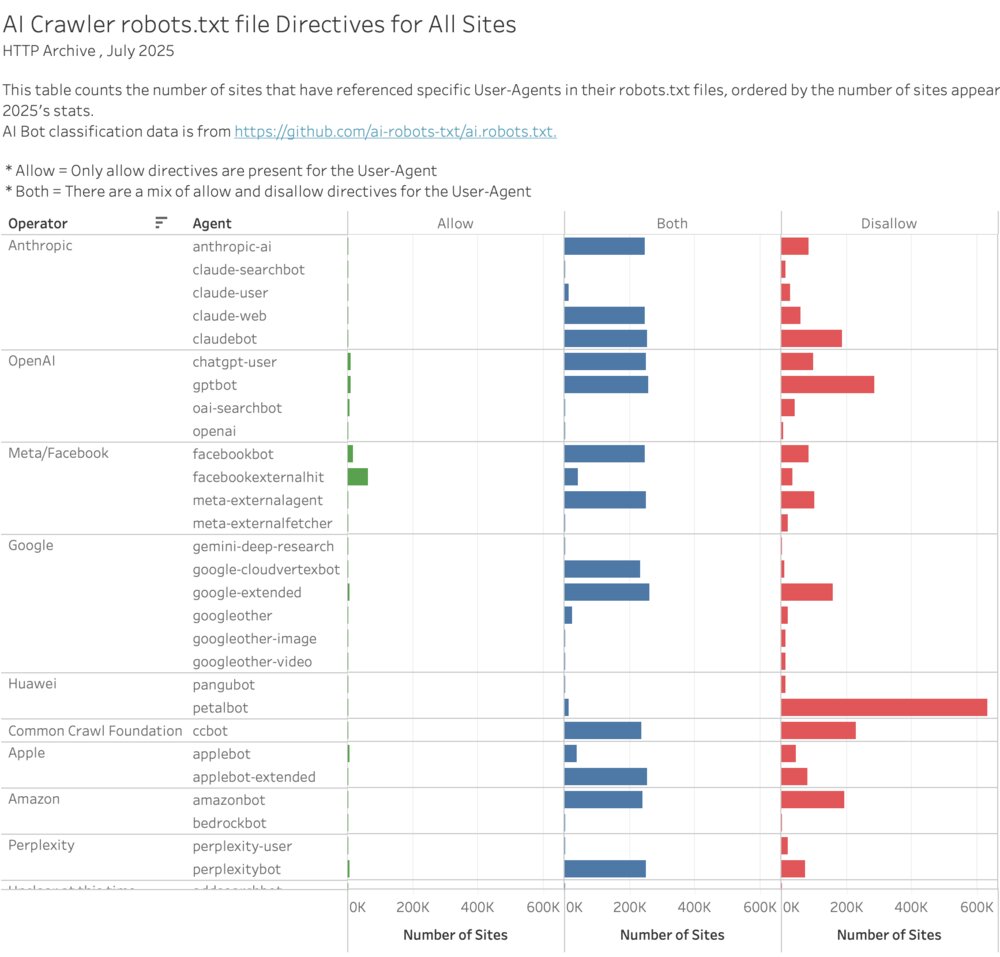
You can explore this data more in these interacitive visualizations:
Conclusion
AI crawlers and bots have become a significant source of synthetic traffic for many sites, and awareness has been growing over the last few years. More and more bots are being introduced which makes it a challenge to keep up. It’s interesting to see how trends in news cause major shifts in website strategy across the web. Often new technologies or features are adopted at a gradual rate. The appearance of the AI bot user agents in so many websites over a short period of time reflects the general sentiment that site owners have towards the scraping of their content for training models.
However, there isn’t uniformity in how AI bots are being treated across the web - especially when compared to the month to month consistency of the SEO and Search agents. The most popular AI services bots appear in more robots.txt files because they have been noticed, and newer ones aren’t picked up as quickly. One can interpret this to show that although the intent to manage how these bots crawl websites is clear, the effectiveness for an individual site is limited to how well each site maintains the list of bots and crawlers.
HTTP Archive queries
This section provides some details on how this analysis was performed, including SQL queries. Please be warned that some of the SQL queries process a significant amount of bytes - which can be very expensive to run. Number of sites containing robots.txt files
This query counts the number of websites that contain a robots.txt file. In order to ensure that we are counting an actual robots.txt file and not error pages, this query only counts robots.txt files that return an HTTP 200 status code and contains one of the following directives: allow, disallow, crawl_delay, noindex, sitemap or user_agent.
SELECT
sites,
sites_with_robots_txt,
ROUND(sites_with_robots_txt / sites,4) AS pct_sites_with_robots_txt
FROM (
SELECT
COUNT(*) AS sites,
COUNTIF(CAST(JSON_VALUE(custom_metrics.robots_txt.record_counts.by_type, "$.allow") AS INT64)
+ CAST(JSON_VALUE(custom_metrics.robots_txt.record_counts.by_type, "$.disallow") AS INT64)
+ CAST(JSON_VALUE(custom_metrics.robots_txt.record_counts.by_type, "$.crawl_delay") AS INT64)
+ CAST(JSON_VALUE(custom_metrics.robots_txt.record_counts.by_type, "$.noindex") AS INT64)
+ CAST(JSON_VALUE(custom_metrics.robots_txt.record_counts.by_type, "$.sitemap") AS INT64)
+ CAST(JSON_VALUE(custom_metrics.robots_txt.record_counts.by_type, "$.user_agent") AS INT64) > 0)
AS sites_with_robots_txt
FROM `httparchive.crawl.pages` AS pages
WHERE date = "2025-07-01"
AND client = "mobile"
AND CAST(JSON_VALUE(custom_metrics.robots_txt, "$.status") AS INT64) = 200
AND is_root_page = true
)
Percent of Sites with User-Agents Appearing in robots.txt Files, by popularity rank
The HTTP Archive stores robots.txt information in a custom metrics object. In this SQL script, we’re UNNESTing each user-agent and then searching for it’s stats within the custom metric.
CREATE TEMP FUNCTION GetByAgent(json STRING, agent STRING)
RETURNS STRING
LANGUAGE js AS r"""
try {
const obj = JSON.parse(json || '{}');
const byua = (((obj || {}).record_counts || {}).by_useragent) || {};
const body = byua[agent] || byua[String(agent).toLowerCase()] || byua[String(agent).toUpperCase()];
return body ? JSON.stringify(body) : null;
} catch (e) { return null; }
""";
WITH robots_txt_ua AS (
SELECT
rank,
page,
agent,
GetByAgent(TO_JSON_STRING(custom_metrics.robots_txt), agent) AS agent_obj
FROM `httparchive.crawl.pages`,
UNNEST(
REGEXP_EXTRACT_ALL(
TO_JSON_STRING(JSON_QUERY(custom_metrics.robots_txt, '$.record_counts.by_useragent')),
r'"([^"]+)":\{'
)
) AS agent
WHERE date = "2025-07-01"
AND client = "mobile"
AND is_root_page = TRUE
),
robots_txt_rule_counts_by_ua AS (
SELECT
rank,
page,
LOWER(agent) AS agent,
agent_obj,
SAFE_CAST(JSON_VALUE(agent_obj, '$.allow') AS INT64) AS allow_cnt,
SAFE_CAST(JSON_VALUE(agent_obj, '$.crawl_delay') AS INT64) AS crawl_delay_cnt,
SAFE_CAST(JSON_VALUE(agent_obj, '$.disallow') AS INT64) AS disallow_cnt,
SAFE_CAST(JSON_VALUE(agent_obj, '$.noindex') AS INT64) AS noindex_cnt,
SAFE_CAST(JSON_VALUE(agent_obj, '$.other') AS INT64) AS other_cnt
FROM robots_txt_ua
),
pages_in_rank_group AS (
SELECT
rank,
COUNT(DISTINCT page) AS total_sites
FROM `httparchive.crawl.pages`
WHERE
date = "2025-07-01"
AND client = "mobile"
AND is_root_page = TRUE
GROUP BY 1
ORDER BY 1
)
SELECT
robots_txt_rule_counts_by_ua.rank,
agent,
total_sites,
COUNT(DISTINCT page) AS sites
FROM robots_txt_rule_counts_by_ua
LEFT JOIN pages_in_rank_group
ON robots_txt_rule_counts_by_ua.rank = pages_in_rank_group.rank
GROUP BY 1,2,3
ORDER BY 1,4 DESC
2023-2025 Trend of Sites with User-Agents Appearing in robots.txt Files
This query builds on top of the previous one, but runs against multiple dates. Warning: As of July 2025, this SQL query processes approximately 330GB of data. Running multiple queries like this can be costly.
CREATE TEMP FUNCTION GetByAgent(json STRING, agent STRING)
RETURNS STRING
LANGUAGE js AS r"""
try {
const obj = JSON.parse(json || '{}');
const byua = (((obj || {}).record_counts || {}).by_useragent) || {};
const body = byua[agent] || byua[String(agent).toLowerCase()] || byua[String(agent).toUpperCase()];
return body ? JSON.stringify(body) : null;
} catch (e) { return null; }
""";
WITH robots_txt_ua AS (
SELECT
date,
page,
rank,
agent,
GetByAgent(TO_JSON_STRING(custom_metrics.robots_txt), agent) AS agent_obj
FROM `httparchive.crawl.pages`,
UNNEST(
REGEXP_EXTRACT_ALL(
TO_JSON_STRING(JSON_QUERY(custom_metrics.robots_txt, '$.record_counts.by_useragent')),
r'"([^"]+)":\{'
)
) AS agent
WHERE
date >= "2023-01-01"
AND client = "mobile"
AND is_root_page = TRUE
)
SELECT
date,
agent,
COUNT(DISTINCT page) AS sites
FROM robots_txt_rule_counts_by_ua
GROUP BY 1,2
HAVING COUNT(DISTINCT page) > 100
ORDER BY 1,3 DESC
AI Bot Directives
This query uses the [AI Robots.txt Github repository](https://github.com/ai-robots-txt/ai.robots.txt){:target="_blank"} to classify User-Agents by AI service. Is then counts the number of sites that include different directives and combinations of directives in their robots.txt files
CREATE TEMP FUNCTION GetByAgent(json STRING, agent STRING)
RETURNS STRING
LANGUAGE js AS r"""
try {
const obj = JSON.parse(json || '{}');
const byua = (((obj || {}).record_counts || {}).by_useragent) || {};
const body = byua[agent] || byua[String(agent).toLowerCase()] || byua[String(agent).toUpperCase()];
return body ? JSON.stringify(body) : null;
} catch (e) { return null; }
""";
WITH bots AS (
SELECT 'AddSearchBot' AS name,'Unclear at this time.' AS operator,'Unclear at this time.' AS respect_robotstxt,'AI Search Crawlers' AS `function`
UNION ALL SELECT 'AI2Bot','Ai2','Yes','Content is used to train open language models.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Ai2Bot-Dolma','Ai2','Yes','Content is used to train open language models.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'aiHitBot','aiHit','Yes','A massive, artificial intelligence/machine learning, automated system.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Amazonbot','Amazon','Yes','Service improvement and enabling answers for Alexa users.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Andibot','Andi','Unclear at this time','Search engine using generative AI, AI Search Assistant'
UNION ALL SELECT 'anthropic-ai','Anthropic','Unclear at this time.','Scrapes data to train Anthropics AI products.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Applebot','Apple','Unclear at this time.','AI Search Crawlers'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Applebot-Extended','Apple','Yes','Powers features in Siri, Spotlight, Safari, Apple Intelligence, and others.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Awario','Awario','Unclear at this time.','AI Data Scrapers'
UNION ALL SELECT 'bedrockbot','Amazon','Yes','Data scraping for custom AI applications.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'bigsur.ai','Big Sur AI','Unclear at this time.','AI Assistants'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Brightbot 1.0','Browsing.ai','Unclear at this time.','LLM/AI training.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Bytespider','ByteDance','No','LLM training.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'CCBot','Common Crawl Foundation','Yes','Provides open crawl dataset, used for many purposes, including Machine Learning/AI.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'ChatGPT Agent','OpenAI','Yes','AI Agents'
UNION ALL SELECT 'ChatGPT-User','OpenAI','Yes','Takes action based on user prompts.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Claude-SearchBot','Anthropic','Yes','Claude-SearchBot navigates the web to improve search result quality.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Claude-User','Anthropic','Yes','Claude-User supports Claude AI users by fetching pages for questions.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Claude-Web','Anthropic','Unclear at this time.','Undocumented AI Agents'
UNION ALL SELECT 'ClaudeBot','Anthropic','Yes','Scrapes data to train Anthropics AI products.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'CloudVertexBot','Unclear at this time.','Unclear at this time.','AI Data Scrapers'
UNION ALL SELECT 'cohere-ai','Cohere','Unclear at this time.','Retrieves data to provide responses to user-initiated prompts.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'cohere-training-data-crawler','Cohere','Unclear at this time.','AI Data Scrapers'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Cotoyogi','ROIS','Yes','AI LLM Scraper.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Crawlspace','Crawlspace','Yes','Scrapes data'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Datenbank Crawler','Datenbank','Unclear at this time.','AI Data Scrapers'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Devin','Devin AI','Unclear at this time.','AI Assistants'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Diffbot','Diffbot','At the discretion of Diffbot users.','Aggregates structured web data for monitoring and AI model training.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'DuckAssistBot','Unclear at this time.','Unclear at this time.','AI Assistants'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Echobot Bot','Echobox','Unclear at this time.','AI Data Scrapers'
UNION ALL SELECT 'EchoboxBot','Echobox','Unclear at this time.','Data collection to support AI-powered products.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'FacebookBot','Meta/Facebook','Yes','Training language models'
UNION ALL SELECT 'facebookexternalhit','Meta/Facebook','No','Ostensibly only for sharing, but likely used as an AI crawler as well'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Factset_spyderbot','Factset','Unclear at this time.','AI model training.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'FirecrawlAgent','Firecrawl','Yes','AI scraper and LLM training'
UNION ALL SELECT 'FriendlyCrawler','Unknown','Yes','We are using the data from the crawler to build datasets for machine learning experiments.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Gemini-Deep-Research','Google','Unclear at this time.','AI Assistants'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Google-CloudVertexBot','Google','Yes','Build and manage AI models for businesses employing Vertex AI'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Google-Extended','Google','Yes','LLM training.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'GoogleAgent-Mariner','Google','Unclear at this time.','AI Agents'
UNION ALL SELECT 'GoogleOther','Google','Yes','Scrapes data.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'GoogleOther-Image','Google','Yes','Scrapes data.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'GoogleOther-Video','Google','Yes','Scrapes data.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'GPTBot','OpenAI','Yes','Scrapes data to train OpenAIs products.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'iaskspider/2.0','iAsk','No','Crawls sites to provide answers to user queries.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'ICC-Crawler','NICT','Yes','Scrapes data to train and support AI technologies.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'ImagesiftBot','ImageSift','Yes','Scrapes the internet for publicly available images.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'img2dataset','img2dataset','Unclear at this time.','Scrapes images for use in LLMs.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'ISSCyberRiskCrawler','ISS-Corporate','No','Scrapes data to train machine learning models.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Kangaroo Bot','Unclear at this time.','Unclear at this time.','AI Data Scrapers'
UNION ALL SELECT 'LinerBot','Unclear at this time.','Unclear at this time.','AI Assistants'
UNION ALL SELECT 'meta-externalagent','Meta/Facebook','Yes','Used to train models and improve products.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'meta-externalfetcher','Meta/Facebook','Unclear at this time.','AI Assistants'
UNION ALL SELECT 'MistralAI-User','Mistral','Unclear at this time.','AI Assistants'
UNION ALL SELECT 'MistralAI-User/1.0','Mistral AI','Yes','Takes action based on user prompts.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'MyCentralAIScraperBot','Unclear at this time.','Unclear at this time.','AI data scraper'
UNION ALL SELECT 'netEstate Imprint Crawler','netEstate','Unclear at this time.','AI Data Scrapers'
UNION ALL SELECT 'NovaAct','Unclear at this time.','Unclear at this time.','AI Agents'
UNION ALL SELECT 'OAI-SearchBot','OpenAI','Yes','Search result generation.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'omgili','Webz.io','Yes','Data is sold.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'omgilibot','Webz.io','Yes','Data is sold.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'OpenAI','OpenAI','Yes','Unclear at this time.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Operator','Unclear at this time.','Unclear at this time.','AI Agents'
UNION ALL SELECT 'PanguBot','Huawei','Unclear at this time.','AI Data Scrapers'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Panscient','Panscient','Yes','Data collection and analysis using machine learning and AI.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'panscient.com','Panscient','Yes','Data collection and analysis using machine learning and AI.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Perplexity-User','Perplexity','No','Used to answer queries at the request of users.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'PerplexityBot','Perplexity','Yes','Search result generation.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'PetalBot','Huawei','Yes','Used to provide recommendations in Hauwei assistant and AI search services.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'PhindBot','phind','Unclear at this time.','AI-enhanced search engine.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Poseidon Research Crawler','Poseidon Research','Unclear at this time.','AI research crawler'
UNION ALL SELECT 'QualifiedBot','Qualified','Unclear at this time.','Company offers AI agents and other related products.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'QuillBot','QuillBot','Unclear at this time.','Company offers AI detection, writing tools and other services.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'quillbot.com','QuillBot','Unclear at this time.','Company offers AI detection, writing tools and other services.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'SBIntuitionsBot','SB Intuitions','Yes','Uses data gathered in AI development and information analysis.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Scrapy','Zyte','Unclear at this time.','Scrapes data for a variety of uses including training AI.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'SemrushBot-OCOB','Semrush','Yes','Crawls your site for ContentShake AI tool.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'SemrushBot-SWA','Semrush','Yes','Checks URLs on your site for SEO Writing Assistant.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Sidetrade indexer bot','Sidetrade','Unclear at this time.','Extracts data for a variety of uses including training AI.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Thinkbot','Thinkbot','No','Insights on AI integration and automation.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'TikTokSpider','ByteDance','Unclear at this time.','LLM training.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Timpibot','Timpi','Unclear at this time.','Scrapes data for use in training LLMs.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'VelenPublicWebCrawler','Velen Crawler','Yes','Scrapes data for business data sets and machine learning models.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'WARDBot','WEBSPARK','Unclear at this time.','AI Data Scrapers'
UNION ALL SELECT 'Webzio-Extended','Unclear at this time.','Unclear at this time.','AI Data Scrapers'
UNION ALL SELECT 'wpbot','QuantumCloud','Unclear at this time.','Live chat support and lead generation.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'YaK','Meltwater','Unclear at this time.','AI-enabled consumer intelligence'
UNION ALL SELECT 'YandexAdditional','Yandex','Yes','Scrapes/analyzes data for the YandexGPT LLM.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'YandexAdditionalBot','Yandex','Yes','Scrapes/analyzes data for the YandexGPT LLM.'
UNION ALL SELECT 'YouBot','You','Yes','Scrapes data for search engine and LLMs.'
),
robots_txt_ua AS (
SELECT
page,
agent,
GetByAgent(TO_JSON_STRING(custom_metrics.robots_txt), agent) AS agent_obj
FROM `httparchive.crawl.pages`,
UNNEST(
REGEXP_EXTRACT_ALL(
TO_JSON_STRING(JSON_QUERY(custom_metrics.robots_txt, '$.record_counts.by_useragent')),
r'"([^"]+)":\{'
)
) AS agent
WHERE date = "2025-07-01"
AND client = "mobile"
AND is_root_page = TRUE
),
robots_txt_rule_counts_by_ua AS (
SELECT
page,
LOWER(agent) AS agent,
agent_obj,
SAFE_CAST(JSON_VALUE(agent_obj, '$.allow') AS INT64) AS allow_cnt,
SAFE_CAST(JSON_VALUE(agent_obj, '$.crawl_delay') AS INT64) AS crawl_delay_cnt,
SAFE_CAST(JSON_VALUE(agent_obj, '$.disallow') AS INT64) AS disallow_cnt,
SAFE_CAST(JSON_VALUE(agent_obj, '$.noindex') AS INT64) AS noindex_cnt,
SAFE_CAST(JSON_VALUE(agent_obj, '$.other') AS INT64) AS other_cnt
FROM robots_txt_ua
)
SELECT
agent,
operator,
respect_robotstxt,
SUM(freq) AS sites,
SUM(IF(directives="both allow and disallow", freq, NULL)) AS both,
SUM(IF(directives="allow", freq, NULL)) AS allow,
SUM(IF(directives="disallow", freq, NULL)) AS disallow,
SUM(IF(directives="crawl_delay", freq, NULL)) AS crawl_delay,
SUM(IF(directives="noindex", freq, NULL)) AS noindex
FROM (
SELECT
agent,
operator,
respect_robotstxt,
CASE
WHEN allow_cnt > 0 AND disallow_cnt > 0 THEN "both allow and disallow"
WHEN allow_cnt > 0 THEN "allow"
WHEN disallow_cnt > 0 THEN "disallow"
WHEN crawl_delay_cnt > 0 THEN "crawl_delay"
WHEN noindex_cnt > 0 THEN "noindex"
ELSE "other"
END as directives,
COUNT(DISTINCT page) AS freq,
FROM robots_txt_rule_counts_by_ua r
JOIN bots b
ON LOWER(r.agent) = LOWER(b.name)
GROUP BY 1,2,3,4
ORDER BY 5 DESC
)
GROUP BY 1,2,3
ORDER BY 4 DESC
